Sometime back I wrote about Collections Framework. Here let me take a slightly deeper look into some of the concrete implementations with examples.
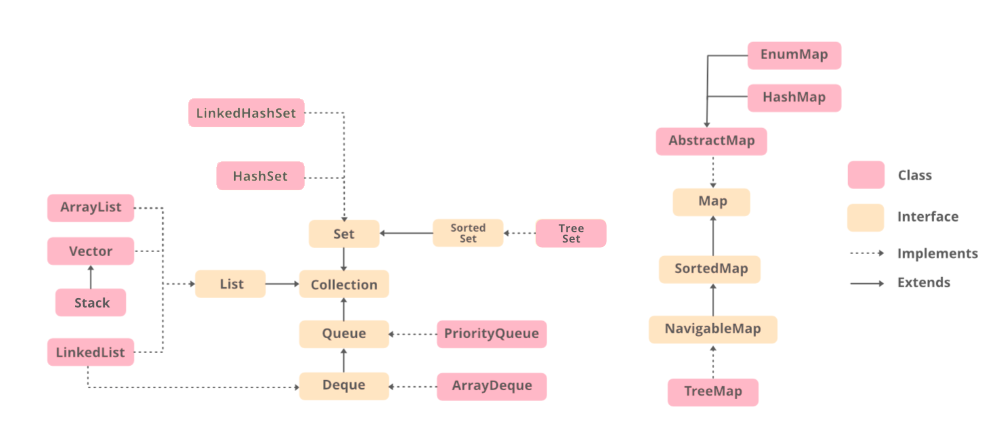
List Implementations
ArrayList: Simply put, this provides dynamic array implementation in Java.
LinkedList: Implementation of Linked List data structure. Provides methods like add and remove.
Vector: It is a synchronized ArrayList.
Stack: Implementation of Stack data structure. Provides methods like push and pop.
Queue Implementations
PriorityQueue: Implement First In, First Out. If Comparator is provided, it will be used for Priority management.
public class PriorityQueueDemo {
public static void main(String args[])
{
PriorityQueue<Integer> pQueue = new PriorityQueue<Integer>();
pQueue.add(10);
pQueue.add(20);
pQueue.add(15);
System.out.println(pQueue.peek());
System.out.println(pQueue.poll());
System.out.println(pQueue.peek());
}
}
Output
10
10
15
Dequeue Implementation
ArrayDequeue: Double-ended queue implementation. Provides methods like add, addFirst, addLast.
Set Implementations
HashSet: Implementation of hash table data structure. Do not guarantee order.
LinkedHashSet: Uses a doubly linked list and hence maintains the order.
Sorted Set Implementation
TreeSet: Ordering is maintained as natural order or explicit comparator based ordering.
public class TreeSetDemo {
public static void main(String args[])
{
TreeSet<String> ts = new TreeSet<String>();
ts.add("this");
ts.add("is");
ts.add("just");
ts.add("a");
ts.add("test");
Iterator<String> itr = ts.iterator();
while (itr.hasNext()) {
System.out.println(itr.next());
}
}
}
Output
a
is
just
test
this
