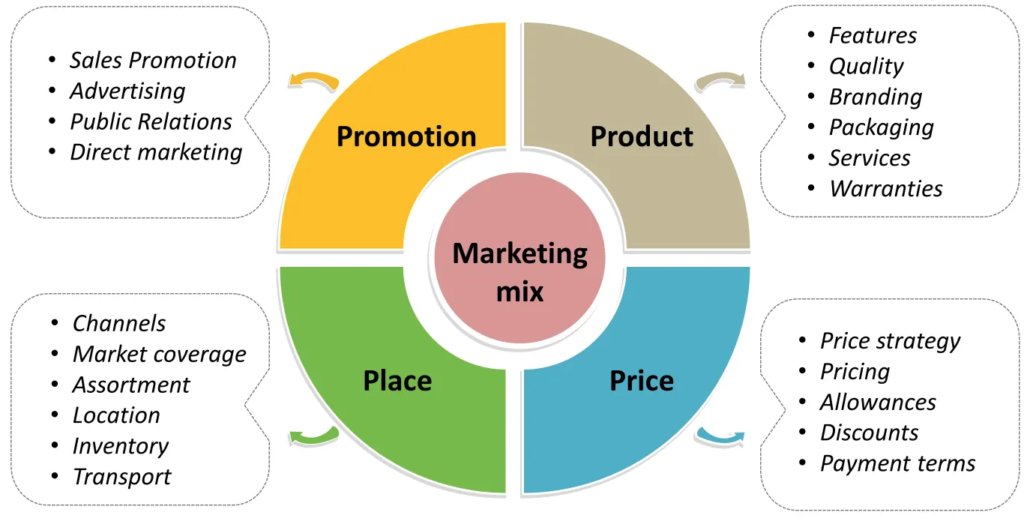
Product
Product Levels

Search Goods: You search and compare characteristics before you buy, for example, in mobile- screen size, camera pixel, features, etc.
Experience Goods: where you can categorize as good or bad after experience only, for example, a stay in a hotel for the first time.
Credence Goods: Where you cannot categorize even after consumption for example an online course (you do not have anything to compare to unless you have taken another course on the subject).
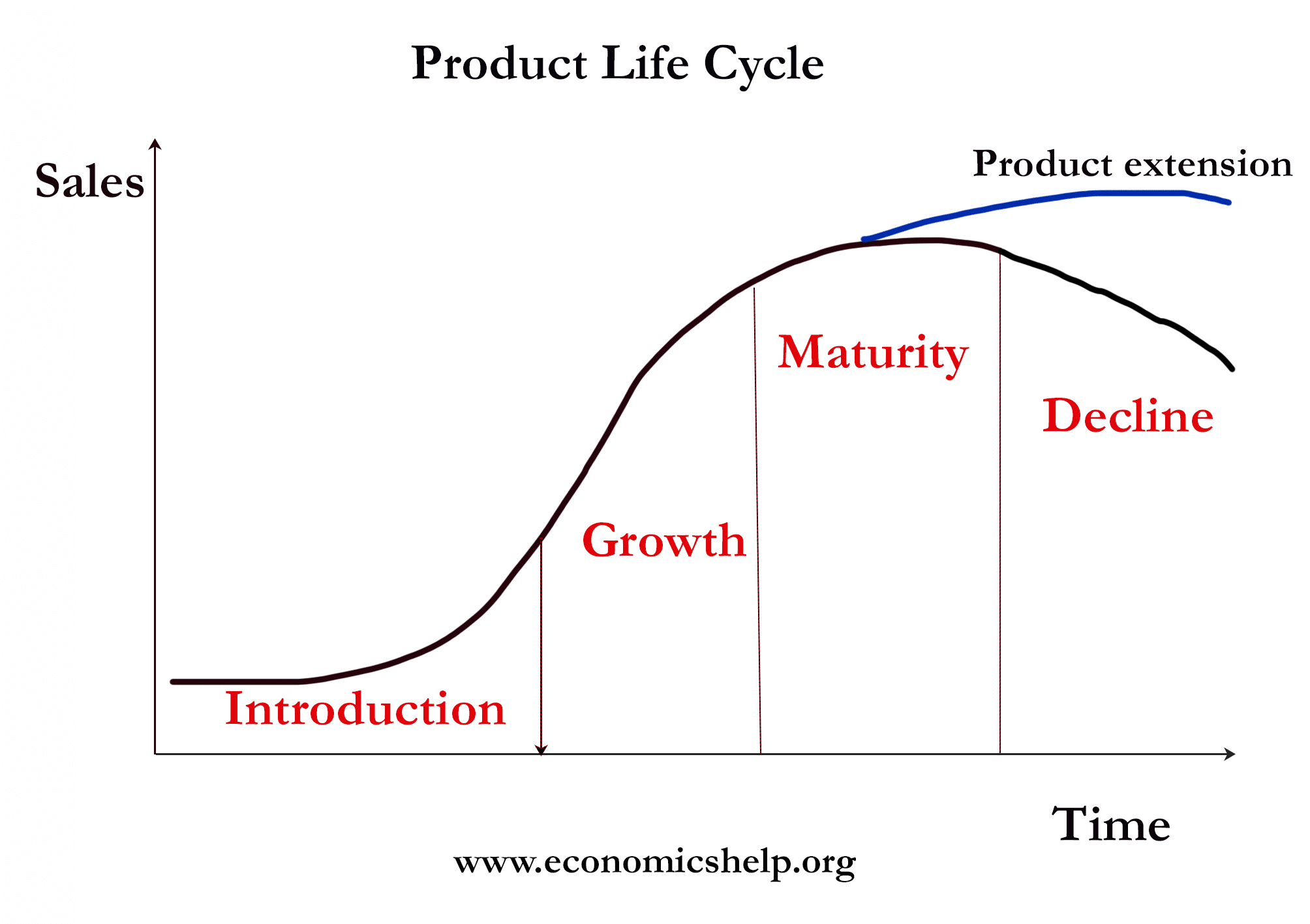
Product Life Cycle or PLC
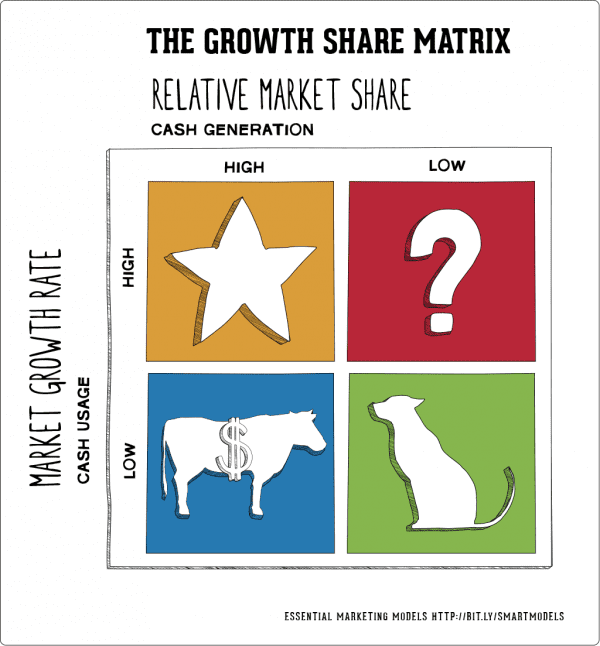
BCG Matrix
Promotion
The second P of marketing is Promotion, which is a basic means for generating awareness about the product and create a desire to buy.
6M strategy model
- Mission: What is the objective?
- Market: Who are my customers?
- Message: What I will tell my customers?
- Media: How do I reach them?
- Money: Budget
- Measure: Was the campaign effective?
Two choices of channels
- Personal Communication: Mostly more effective and low price via Telemarketing, Emailing or one on one meetings.
- Impersonal communication: Mass media via Newspaper or T.V.
Place
The third P of marketing is Place. This gives the convenience of product availability at an arm’s length and helps build trust with customers.
Price
The fourth P of marketing is Price. A fundamental mistake done by companies is to think of price as cost + profit. Ideally one needs to do market research and competitive analysis to come up with the target price. Once one has a target price, it helps to come up with a target cost and help figure out how much to be spent on RnD, marketing, manufacturing, etc.
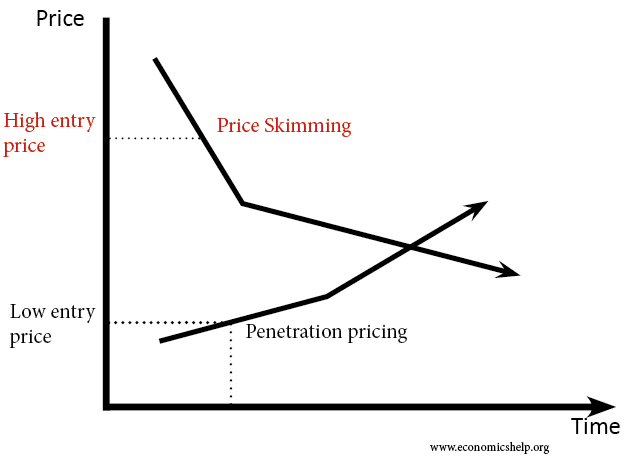
Two common pricing strategies are skimming (enter high and then move to low) and penetration (enter low and move to high).
Going rate pricing is another strategy where current pricing is studied in the market and an average is taken for pricing the product.
